Introduction
In the previous article, we explored aerospace and defense industry ETFs, including XAR, UFO, and ARKX.
https://tenbaggerexplorer.com/saerospace-xar-ufo-arkx
With the election of President Trump, U.S. defense-related stocks experienced a rise. Let’s delve into the reasons for this trend:
Why Are Defense Stocks Rising?
Expectations of Increased Defense Budget: Trump has consistently emphasized strengthening military power, making it highly likely that the defense budget will increase. During his first term, the defense budget grew significantly, and it is expected to rise again in his second term.
Among the ETFs analyzed, a common stock with a significant weight was Rocket Lab USA Inc. (RKLB). While its recent stock price surge has influenced its weight in these ETFs, it is noteworthy that all three ETFs include Rocket Lab to some extent.
Why is Rocket Lab Surging?
One reason for Rocket Lab’s rise is heightened expectations for a new space era following Trump’s election and speculation about Elon Musk’s involvement in government efficiency initiatives. But will this new space age truly arrive? If so, how soon and to what extent?
Before we answer these questions, let’s first examine the global rocket propulsion market and the development of the space industry.
Global Rocket Propulsion Market & Space Industry Development
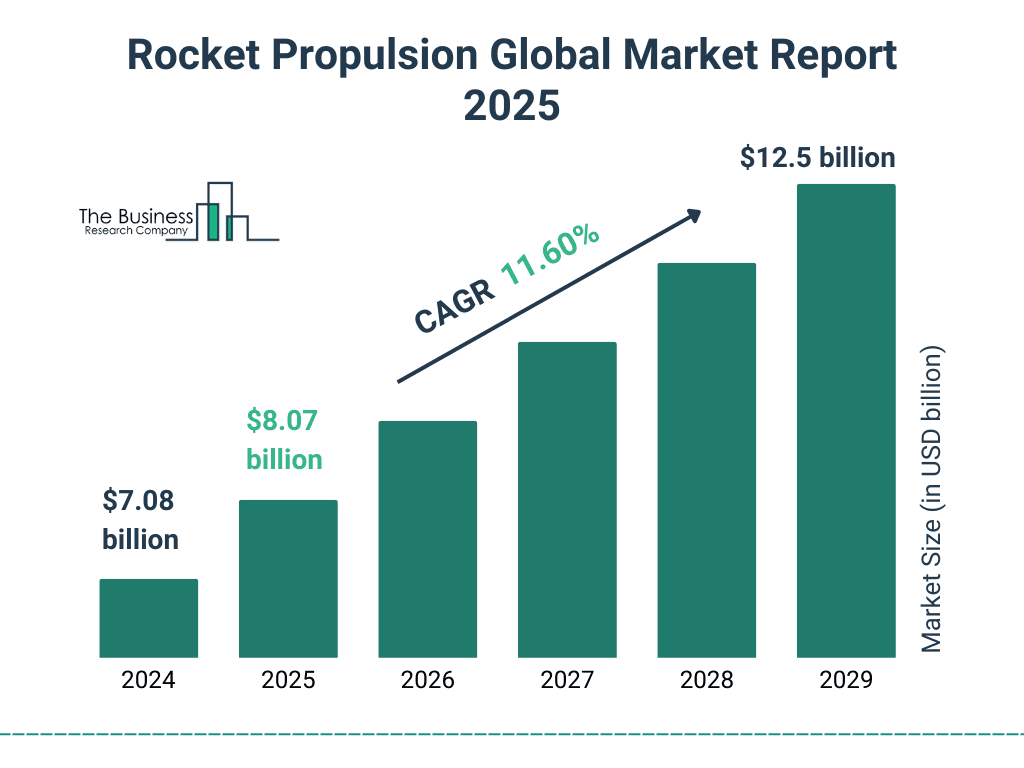
Source:https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/rocket-propulsion-global-market-report
According to a report by The Busubess Research Company, the global rocket propulsion market is projected to grow from $8.07 billion in 2025 to $12.5 billion by 2029, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.60%. This suggests steady annual growth.
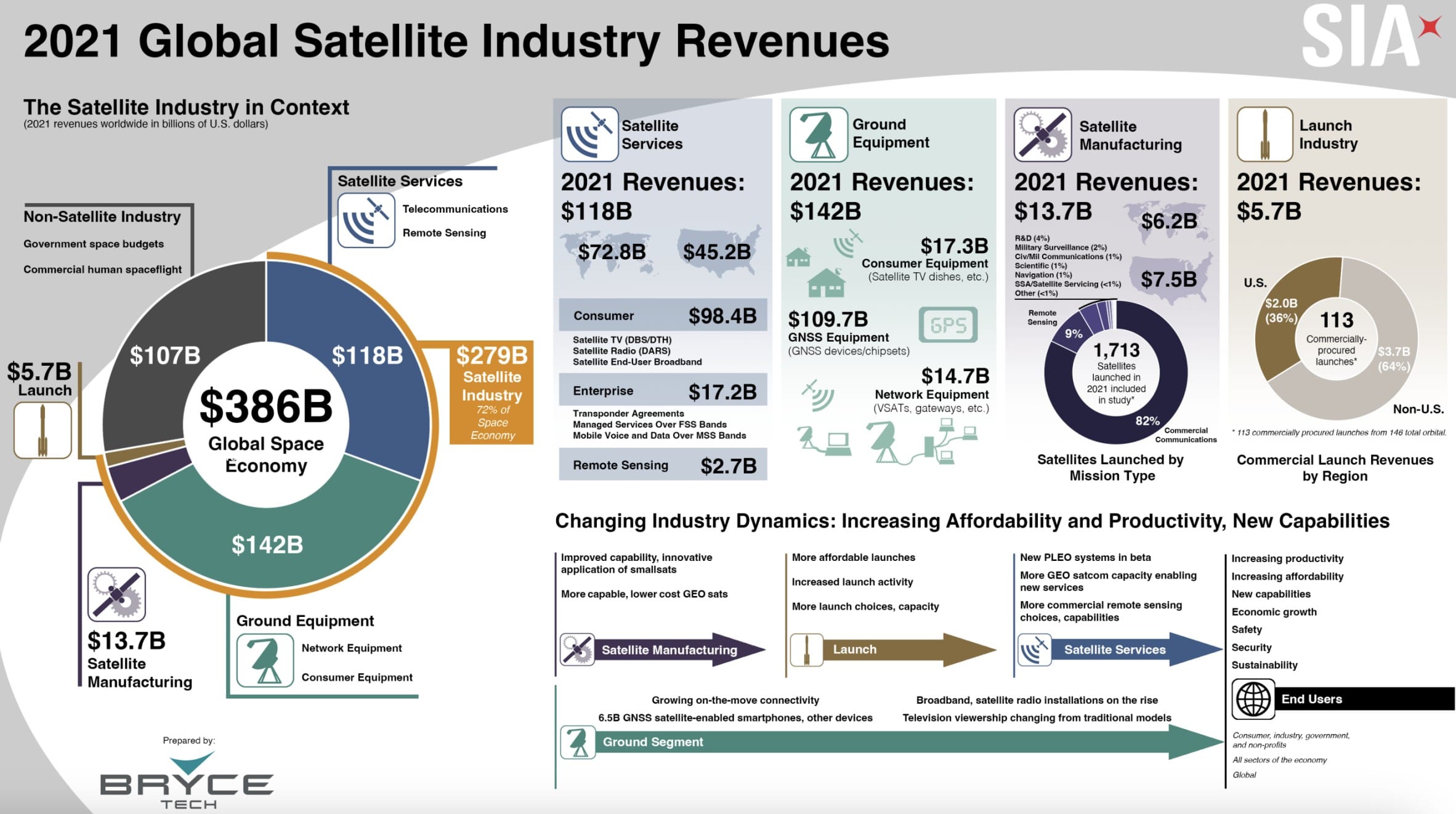
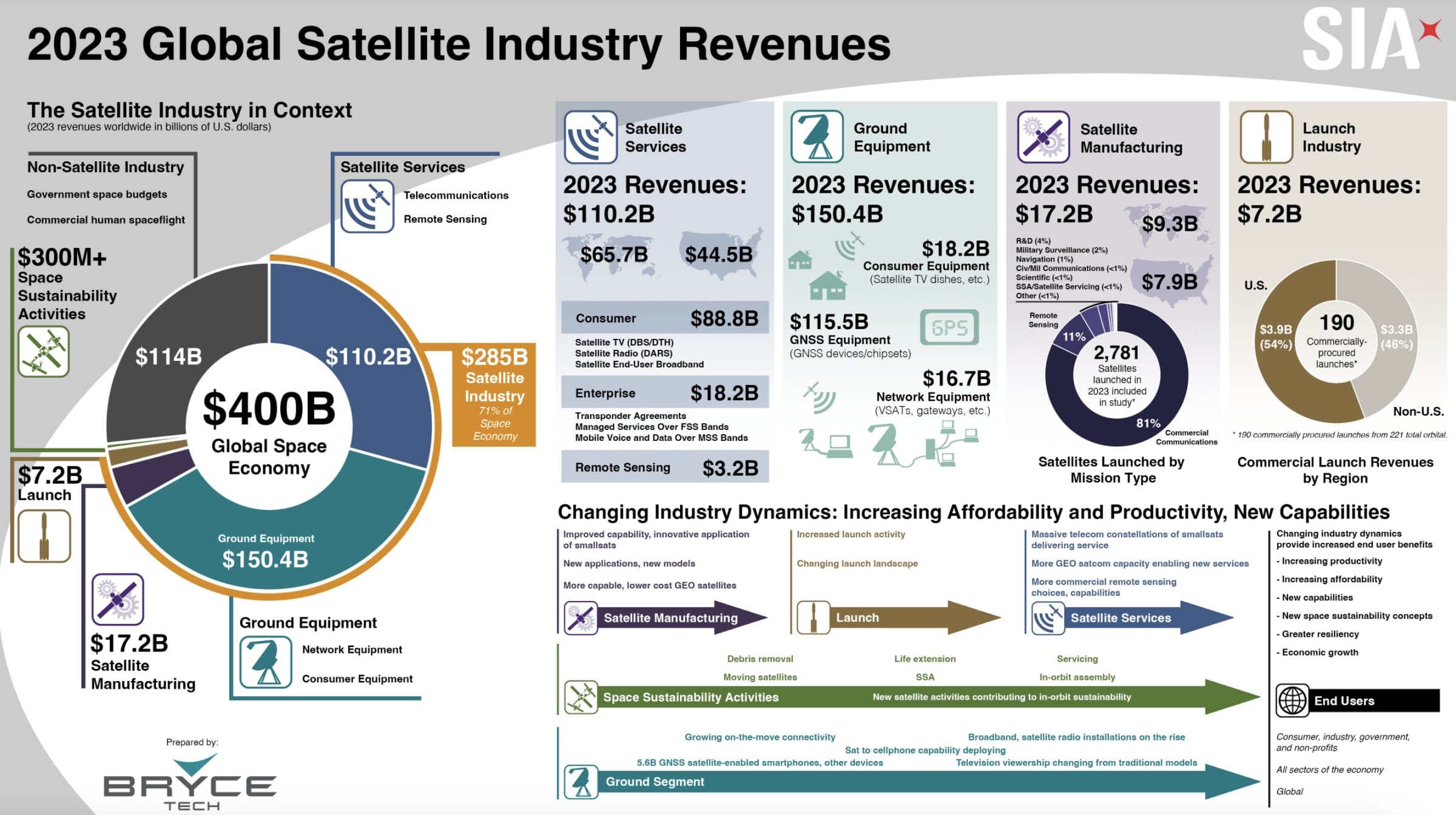
Comparison of 2021 vs. 2023 Global Space Industry Data
2021 Data Source : Satellite Industry Association report
2023 Data Source: Satellite Industry Association report
Since the translated 2021 data is somewhat outdated, it should be used only to understand the industry’s structure. When compared with 2023 data, the total value of the space industry grew from $386 billion to $400 billion. The satellite services sector declined, whereas non-satellite industries, ground equipment, satellite manufacturing, and launch services all increased.
Why Did Satellite Industry Revenue Decline?
The revenue decline in the satellite industry does not indicate stagnation but rather a positive shift resulting from cost reductions due to technological advancements. Innovations such as miniaturized satellites, reusable rocket technology, and enhanced data processing capacity have accelerated. The emergence of vertically integrated private companies (SpaceX, Blue Origin, Rocket Lab) has driven down costs for satellite manufacturing, launch services, and utilization, creating the illusion of stagnant revenue growth.
Despite lower costs, satellite manufacturing and launch revenue actually increased in 2023, mainly due to higher production volumes and an increase in launch frequency.
1. Company Overview
Rocket Lab USA Inc. (NASDAQ: RKLB) is an innovative U.S. space company founded in 2006 by New Zealand engineer Peter Beck. The company is headquartered in Long Beach, California, with additional operations in New Zealand.
Rocket Lab specializes in spacecraft and satellite manufacturing, reliable launch services, and on-orbit management. It operates as a vertically integrated space company, offering end-to-end solutions for space missions, from manufacturing to launch and mission operations.
2. Rocket Lab’s Core Business Areas
A. Small Satellite Launch Services
-
Provides launch services for small satellites (≤300kg) using the Electron rocket.
-
Holds over 50% market share in the commercial small rocket market.
B. Spacecraft & Satellite Manufacturing
-
Designs and manufactures small satellites through the Photon platform.
-
Develops and operates military satellites.
C. Space-Related Software & Components Development
-
Supplies key spacecraft components, including star trackers, reaction wheels, solar panels, satellite radios, and separation systems.
-
Provides flight and ground software solutions.
D. On-Orbit Management Services
-
Offers satellite operations and data services.
-
Provides mission management and support for space operations.
3. Rocket Lab’s Products
A. Electron Rocket
-
A two-stage rocket designed for small satellite launches.
-
Height: 18m | Diameter: 1.2m | Payload Capacity: Up to 300kg to Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
-
Launch Cost: ~$7.5M, significantly lower than SpaceX’s Falcon 9 ($67M).
-
However, cost per kg is $25,000, much higher than Falcon 9’s sub-$5,000 per kg.
-
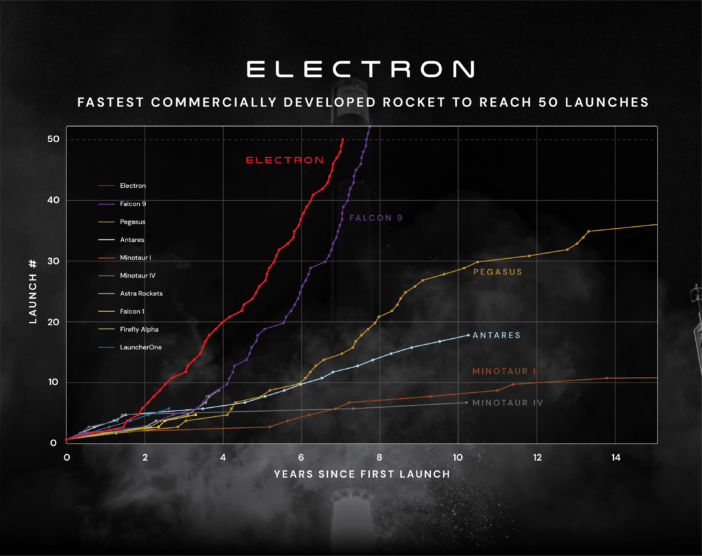
Fastest small rocket to reach 50 launches and the third most-launched rocket globally in 2024.
-
Developing first-stage booster recovery and reusability to further reduce costs and increase launch frequency.
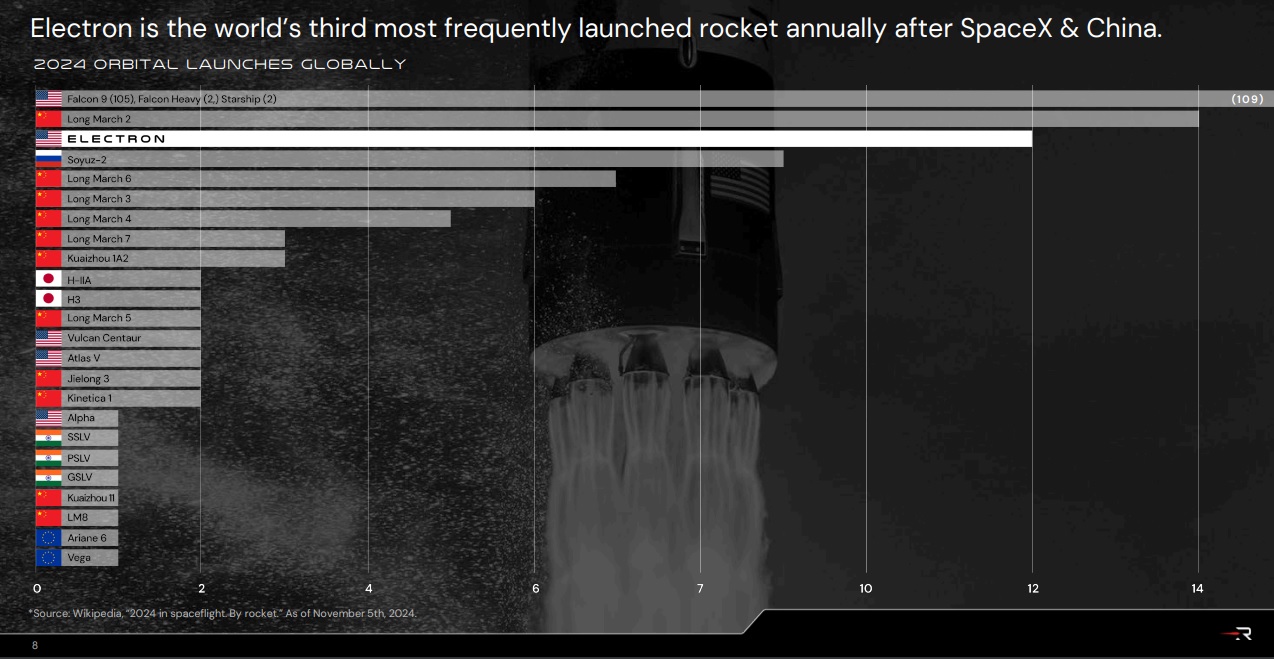
Source: Company Reports
B. Neutron Rocket (Under Development)
- First launch targeted for mid-2025.
- Payload Capacity: Up to 13 tons to LEO.
- Designed for reusability, making it suitable for launching large satellites and mega-constellations.
- Estimated launch cost: $50M–$55M.
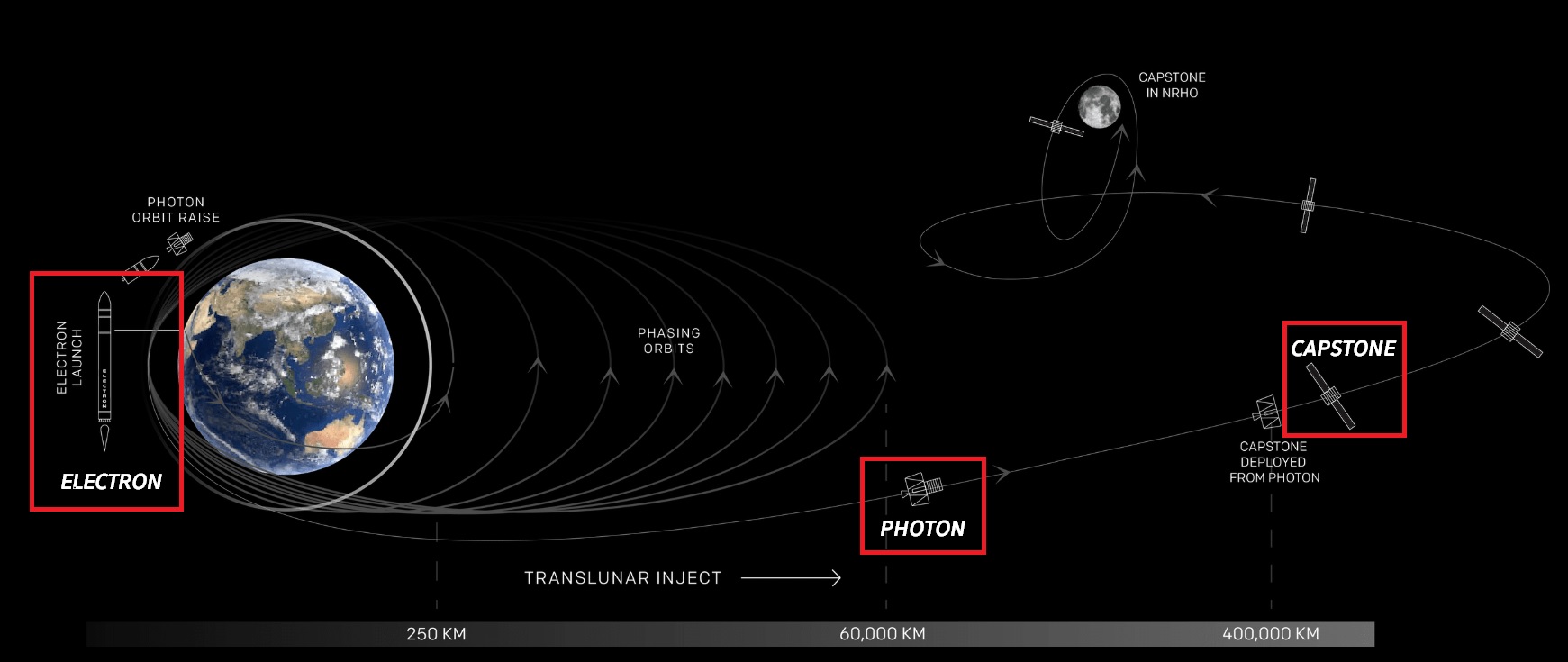
C. Photon Spacecraft
- An innovative small satellite bus designed for diverse missions in LEO.
- Equipped with power, propulsion, and communication capabilities.
- Supports commercial, defense, and scientific applications.
- In December 2025, Rocket Lab plans to launch a Photon spacecraft to Venus to deliver a laser-tunable mass spectrometer for atmospheric research.
Photon’s Key Advantages:
- Reduces development time for customers by providing a ready-to-use satellite platform.
- Integrated launch and spacecraft platform, minimizing risks and development cycles.
- Supports various payloads, including Earth observation and communications equipment.
- Ideal for technology demonstration before deploying large satellite constellations.
4. Financial Performance
A. Revenue Growth
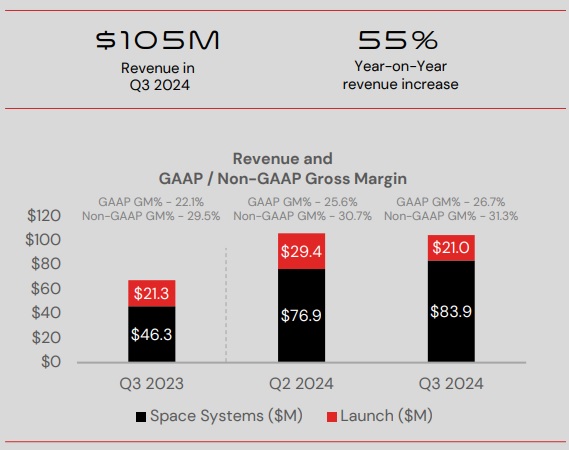
- Revenue increased 55% year-over-year ($37.1 million increase).
- Growth primarily driven by the expansion of the Space Systems business.
- Q3 gross margin improved due to a shift in product mix favoring higher-margin components such as solar panels and separation systems.
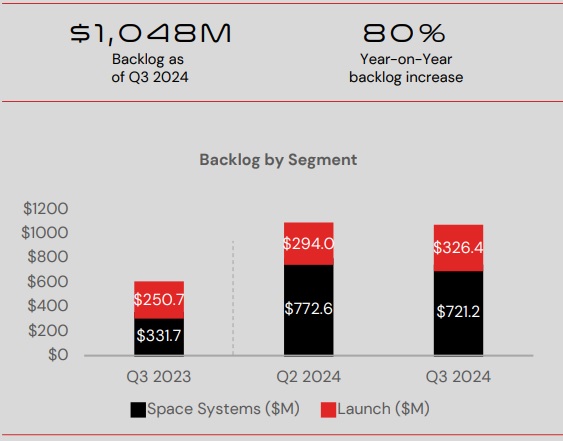
B. Increasing Backlog Trend
- Backlog refers to orders received but not yet fulfilled.
- Key backlog growth drivers:
- Secured contracts under the Space Development Agency (SDA) Beta program.
- Strong bookings for Electron rocket launches.
- Backlog realization forecast:
- 50% expected to be fulfilled within 12 months.
- The remaining 50% will be realized over a longer timeframe.
- Balanced portfolio between Space Systems and Launch Services, ensuring stable revenue streams.
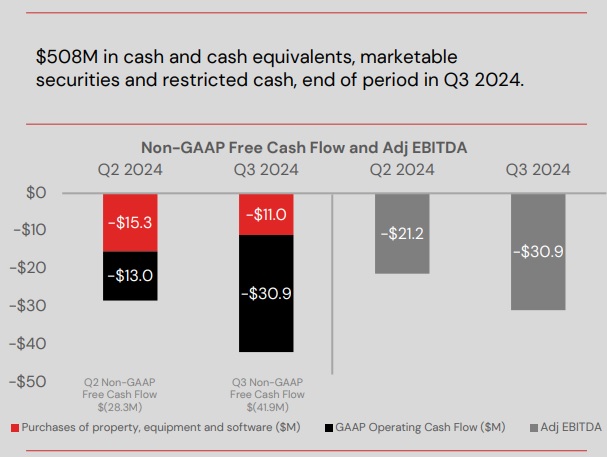
C. Free Cash Flow and EBITDA
- Cash reserves (Q3 2024): $508 million, including cash equivalents and marketable securities.
- Key cash flow changes:
- Capital expenditures decreased by $4.3 million quarter-over-quarter.
- Operating cash flow increased by $17.9 million due to working capital improvements.
- Adjusted EBITDA loss narrowed by $9.7 million, reflecting improved cost efficiencies.
5. Competitive Advantages
A. Vertical Integration Strategy
- End-to-end control over rocket design, manufacturing, launch, and mission management.
- Reduces dependency on third-party suppliers, leading to cost efficiency and quality control improvements.
- 90% of rocket components are produced in-house.
B. Specialization in the Small Satellite Market
- Electron rocket dominates the ≤300kg small satellite launch segment.
- Modular design enables rapid adaptation to evolving customer needs.
- Competitive pricing and fast launch cycles (1.5 launches per month, with 2 launches per month as the breakeven target).
C. Flexible Launch Infrastructure
- Launch sites in New Zealand and Virginia allow high-frequency launch capabilities (up to 132 launches per year).
- Enables customized launch solutions tailored to client requirements.
D. Technological Innovation
- Pioneering reusable rocket technology for Electron and Neutron.
- Photon spacecraft platform enhances mission flexibility.
- Investment in 3D printing technology reduces manufacturing costs and speeds up production cycles.
6. Comparison with SpaceX
| Feature | Rocket Lab | SpaceX |
|---|---|---|
| Market Focus | Small satellite launches | Large satellite launches |
| Main Rocket | Electron | Falcon 9, Falcon Heavy |
| Neutron Rocket | Targets mid-sized payloads (13,000kg) | Competes with Falcon 9 |
- Rocket Lab and SpaceX do not directly compete in the small satellite market.
- Neutron’s debut in 2025 may introduce competition in the medium-payload sector.
7. Risk Factors
A. Operational and Technical Risks
- Electron launch failures or Neutron development delays may harm credibility.
- Rapid growth could introduce operational inefficiencies.
B. Financial Risks
- High R&D and capital expenditure requirements could strain financial stability.
- Potential share dilution if additional funding is required.
C. Market and Competitive Risks
- Increasing competition in the space sector may impact pricing power and market share.
- Heavy reliance on government contracts exposes the company to policy shifts.
D. Regulatory and Legal Risks
- Compliance with international space regulations could increase costs and complexity.
- Intellectual property disputes may arise from ongoing innovation efforts.
E. Environmental Risks
- Rising levels of space debris could negatively impact future launch schedules.
8. Future Vision & Outlook
A. Market Expansion
- The global space economy is projected to grow from $5.14 billion in 2022 to $10.87 billion by 2032.
- Opportunities in satellite communications, Earth observation, navigation, and space tourism.
- The space tourism market alone is expected to reach $4–6 billion by 2035.
B. Growth in Launch Services
- Rocket Lab plans to increase Electron launch frequency to 22–25 times annually by 2025.
- Expansion of Neutron launch services in 2026 to drive higher per-launch revenue.
C. Neutron Rocket Development
- First commercial launch in 2026.
- Revenue per launch is expected to be 4x that of Electron.
- By 2027, Neutron launches could contribute 50% of total revenue.
D. Expansion into Defense Contracts
- Secured a $515 million contract with the U.S. Space Development Agency (SDA).
- Supplying 18 data relay satellites for national security missions in 2025.
E. Financial Growth Expectations
- Projected revenue growth: +40.4% in 2025.
- First GAAP-positive year expected in 2027.
9. Two-Minute Pitch
Peter Lynch emphasized the importance of being able to deliver a two-minute pitch about a stock you are interested in, including the reasons for buying it, the company’s prospects, and its story. If you have thoroughly researched and can confidently articulate this two-minute pitch, you may consider purchasing the stock.
(Note: All investment decisions and responsibilities rest solely with you. Always invest with surplus funds and focus on long-term investments.)
Rocket Lab is a leading player in small satellite launches with strong growth potential. Its Electron rocket is well-established, and the upcoming Neutron rocket will expand its market reach. Despite high R&D and operational costs, the company is steadily increasing revenue, expanding its backlog, and securing government contracts.
Key Takeaways:
- Market Positioning: Specialized in small and medium satellite launches.
- Competitive Edge: Vertical integration, reusable rockets, and flexible launch infrastructure.
- Growth Prospects: Neutron’s debut, defense contracts, and space economy expansion.
- Financial Outlook: Expected profitability by 2027, driven by increasing launch frequency and new revenue streams.
If you believe in Rocket Lab’s potential and can hold for 5–10 years, it could be a strong long-term investment. However, investors should be aware of the risks associated with new technology development and financial sustainability.









0 Comments